Open source tools
fortiss provides software solutions as open source for general use. The source code is freely accessible for further processing under various license models, free of charge and at any time. It can be reproduced and modified within this framework.
The fortiss open source software was developed as part of research projects and is based on solid scientific findings. It serves as a valuable resource for testing innovative approaches in the application areas of mobility, energy, health, production and public administration.
The open source offerings from fortiss simplify access to current research results and are available to the developer and scientific community as well as software developers in the industrial environment. fortiss GmbH assumes no liability for the use of these research prototypes.
In addition, fortiss derives training opportunities for students and training measures for companies from the knowledge and technology transfer offer.
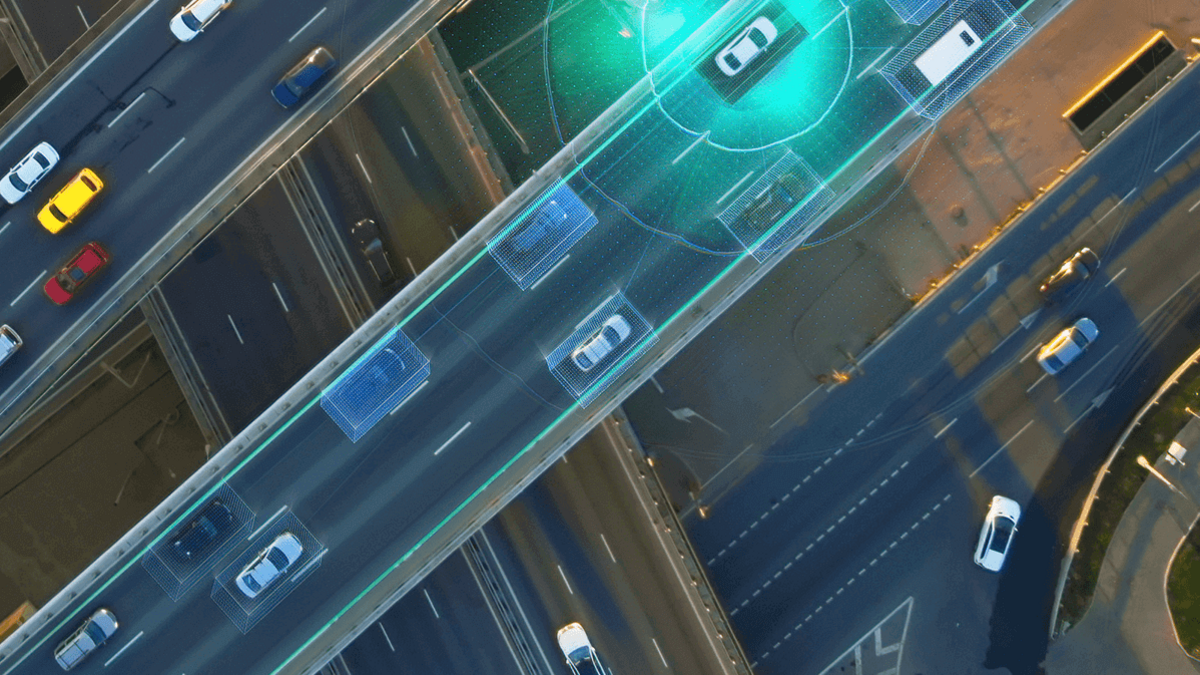

Open source solution for autonomous driving
Road tests are indispensable for validating and demonstrating research algorithms in the field of autonomous driving. The fortiss researchers integrate scientific results into the Apollo software to enable testing of the behavior of autonomous vehicles on the road. Apollo is open source, offers a complete stack of functions for autonomous driving, and is an excellent basis for further research activities.

Model-based development of embedded systems
AutoFOCUS 3 is an open-source tool for model-based engineering of cyber-physical systems. As a research platform, it offers advanced approaches for the development and validation of systems, e.g., architecture exploration, (co-)simulation, assurance cases, reuse and variability, model quality. It supports standards such as SysML and FMI and is successfully used in case studies, especially in the automotive and aerospace industries, as well as in teaching and training.

A framework for behavior modelling and development of autonomous vehicles
The BARK software platform enables the modularized, systematic development of behavior planning components for autonomous systems with a focus on autonomous driving. Behaviormodels developed in BARK can be used for planning as well as for prediction and simulation. The software supports the application of both classic and more modern methods of artificial intelligence.
Cognitive Decentralised Edge Cloud (CODECO) OSS Basic Operation Toolkit v2.0
The CODECO Basic Operation Toolkit v2.0 corresponds to an open-source orchestration framework for containerized applications. Developed to be used with Kubernetes, CODECO brings intelligence to the orchestration of containerized applications via a cognitive, data-compute-network approach to the understanding of what an Edge-Cloud infrastructure is.

NS-3 simulation framework for deterministic wireless/wired networks
The ns-3 DetNetWiFi framework has been developed by the fortiss IIoT team as part of industrial and research projects focusing on deterministic wireless. The simulation environment considers overlapping Wi-Fi6 networks (multi-AP environments) connected to a fixed (Ethernet/TSN) core to enable advanced IoT applications in the context of flexible industrial IoT environments.

A Tool Support for Continuous Assurance Case Creation
ETB2 is a framework for defining and executing distributed assurance workflows that produce claims supported by evidence. ETB2 enables cost- and time-effective creation and continuous maintainance of assurance cases. ETB2 consists of components that work together to enable an end-to-end, decentralized and continuous safety assurance process where multiple entities are involved to establish safety claims supported by arguments and evidence.

Open source 3D simulator for neural network controlled robots
The Neurorobotics Platform is a simulation software for controlling virtual 3D robots with various types of neural networks. The platform is available online or can be installed on a computer. It uses Gazebo as the underlying robot simulator and supports Nest, Spinnaker, Pynn, Nengo, Tensorflow as neural network simulators.

Open source toolbox to support safety engineering of neural networks
The Neural Network Dependability Kit is an open source toolbox to support the data-driven development of neural networks for safety-critical domains. It provides demonstrable reduction of uncertainties in key phases of the product lifecycle, from data acquisition, training, and validation to testing, generalization and operation. The toolbox consists of reliability metrics, formal proof routines and runtime monitoring.

A guardrail framework for safe and secure interaction with Large Language Models
OpenGuard is a guardrail framework that enforces user-defined rules to ensure safe and secure interactions with Large Language Models (LLMs). It detects factual hallucinations by combining Beam Search Sampling (BSS) with Semantic Consistency Analysis, leveraging Natural Language Inference (NLI) and a scoring mechanism based on token probabilities and semantic similarity.

Software for working with the Marktstammdatenregister (MaStR)
The significance of Open Data is steadily increasing in the context of modeling energy systems. The Python package open-MaStR enables the simple download and cleaning of data from the "Marktstammdatenregister" database, which provides detailed information on every electricity and gas plant in Germany.

A Modular Framework for Search-based Testing of Automated Driving Systems
OpenSBT is a modular and extensible framework that enables the integration of simulators with an embedded system under test, search algorithms and fitness functions. The open source tool facilitates the search-based testing of automated driving systems and provides several functionalities.

Smart Energy Systems Simulation Framework
The SESSIM Framework is a co-simulation environment for the analysis of applications in the energy sector for operational optimization with interfaces to EMS or higher-level energy management systems. The aim of the software is to develop fast, platform-compatible prototypes and to integrate these with our partners in their projects.

Making variability manageable in production
The Smart Factory Information Tool (SFIT) implements a methodology developed by fortiss for production planning in the context of Industry 4.0 in a model-based tool. SFIT enables all the relevant aspects of production facilities and products to be recorded in a structured manner. On this basis, a universal approach to variability management makes it possible to efficiently check the manufacturability of any product variants.

Platform for prototyping and evaluating operating system concepts in real-time environments
toki is a simple and easy-to-use prototyping platform for embedded real-time systems for easy evaluation of operating system concepts in industrial applications. With its architecture, which was chosen to be similar to that of industrial production systems, the software provides the basis for implementing early prototypes of research results for real-time systems up to technology readiness level 7 with little effort.

ML semantic matchmaking between IoT things and IoT services
TSMatch is an open source fortiss Edge-based middleware that supports semantic matchmaking between semantic descriptions of IoT devices and of IoT services. The main goal of TSMatch is to automate the IoT data exchange while meeting the requirements of the services. To this end, TSMatch follows an ML-based semantic matchmaking approach based on Natural Language Processing with a Neural-network model.